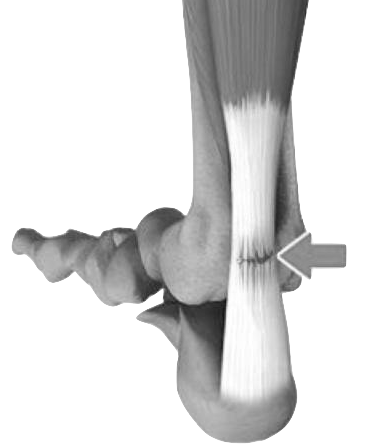
Achilles Tendon Problems
What is the Achilles Tendon?
The Achilles Tendon is a band of soft but fibrous tissue that combine to form a strong tough cord.
This Achilles Tendon is one of the longest tendons in your body. It stretches from the heel bone to your calf muscles.
Contraction of the calf muscles tightens the Achilles Tendon and pulls the heel. This function enables the heel, foot and toe movements necessary for walking, running and jumping.
Types of Achilles Tendon Problems
Tendon problems or Tendinopathies, are also known as tendinitis or tendinosis common types include:
- Achilles Tendon Rupture - tears (rupture) of tendon
- Achilles Tendinosis - chronically damaged tendon with a loss of structure (disorganized, hard, thickened, scarred fibres with rubbery appearance)
- Achilles Tendinitis - acutely inflamed and swollen tendon that doesn't have microscopic tendon damage
- Achilles Paratenonitis - acute inflammation of the covering of the Achilles tendon
- Achilles
Tendon Bursitis - also referred to as retrocalcaneal bursitis is the swelling of the bursa
| Phase | Name | Tendon Change | Prognosis |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | Reactive Tendinopathy | Normal Tissue Adaptation | Excellent - no or minimal treatment required |
| II | Tendon Dysrepair | Diminished load rate & Cell Loss | Good - Tendinopathy rehab program |
| III | Degenerative Tendinopathy | Diminished load rate & Cell Loss | Moderate - Tendinopathy rehab program |
| IV | Tendon Tear / Rupture | Tendon Tissue Breakdown | Loss of Function - surgery required |
About Achilles Tendinosis
Achilles Tendinosis is the degeneration of the Achilles tendon due to unresolved inflammation. The tendon develops minute tears or pores in the tissue, losing its unique structure. Sometimes, because of degeneration, an Achilles tendon also tears or ruptures partially or completely, causing pain or loss of movement.
About Achilles Tendinitis
Also referred to as Achilles tendinopathy is a common overuse injury and can be classified into two categories, these are
- Non-Insertional Achilles Tendinitis - acutely inflamed and swollen tendon that doesn't have microscopic tendon damage
- Insertional Achilles Tendinitis - degenerated tendon where it connects to the heel bone caused by exertion of force or repeated stress
Insertional Achilles Tendinitis commonly occurs in people between the ages of 40-50 years it is typically an overuse injury but also exacerbated by other inflammatory conditions that can be caused by: spondyloarthropathy, gout, psoriasis, Reiter’s syndrome, sarcoidosis, familial hyperlipidaemia, diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis and some medications such as steroids and certain antibiotics.
About Achilles Paratenonitis
Achilles Paratenonitis is also known as Achilles Peritendinitis, Tendovaginitis or Tenosynovitis. Achilles Paratenonitis can cause scarring that restricts the motion of the Achilles tendon but respond well to pain management. Achilles Paratenonitis occurs due to acute repeated straining of the Achilles tendon. The sheath becomes severely inflamed due to the overuse and becomes very painful.
About Achilles Tendon Bursitis
The retrocalcaneal bursa, a fluid-filled sac, which is located at the back of the heel under the Achilles tendon, contains a lubricating fluid that acts as a cushion to reduce friction between muscle and bones. Achilles tendon bursitis can occur in conjunction with Achilles Tendinitis or as a secondary injury associated with chronic conditions such as Plantar Fasciitis, Heel Spurs, Fibromyalgia and Rheumatoid arthritis.
About Achilles Tendon Rupture
The tear or rupture of the Achilles Tendon is commonly seen in people who are involved in sports activities. People with a history of Tendonitis, and certain diseases such as Diabetes, are at higher risk for Achilles Tendon Rupture.
What Causes Achilles Tendon Problems?
Common causes of Achilles Tendon Injuries include:
- Overuse - repetitive activities that exert excessive stress on the tendon and lead to micro-tears
- Foot Stressful Activities - participating in sports, exercises and occupation where pressure on the feet and ankles
- Footwear - improper shoes can also result in the rupture of the tendon.
- Obesity - places more strain on many parts of the body including the Achilles tendon
Symptoms of Achilles Tendon Problems
Symptoms related to Achilles tendon disorders include:
- Swelling and bruising
- Mild tenderness at the back of the heel to severe pain (Rupture)
- Stiffness
- Loss of strength with decreased movement of the ankle
- Muscle weakness or tenderness
- Difficulty standing on tiptoe or pushing leg while walking
A popping or snapping sound may be heard when an Achilles Rupture occurs.
How are Achilles Tendon Problems Diagnosed?
Medical History
Your doctor will ask questions about:
- Current symptoms and their severity
- If an injury was sustained
- Your medical history including family or genetic links
- Your current and past medications
- The impact of the problem on your occupation and lifestyle
Physical Examination
Your doctor perform comprehensive physical evaluation that will include:
- Examining the affected area for swelling, pain, bruising or other features
- Assessing your range of motion, walking pattern and other relevant features
Diagnostic Testing
Once your doctor has completed the physical examination further tests maybe required. These tests can help your doctor determine or eliminate possible causes. These can include:
- X-Ray
- Ultrasound (US)
- Computerised Tomography (CT)
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
Once a final diagnosis has been completed your doctor can discuss with you and recommend any treatment options.
Non Surgical Treatment for Achilles Tendonitis
Treatment for your condition is dependent on the cause, but can broadly include:
- Rest: Resting the affected area or pausing athletic activity until the symptoms have faded
- Pain medication: Paracetamol or Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs) can relieve some pain or discomfort
- Physiotherapy: A specific program will be recommended such as the Heel Drop Protocol for Achilles Tendinitis.
- Shoewear modification: More supportive shoewear may benefit
- Orthotics: Such as a heel cup or heel raise may help in reducing pain.
- Extracorporeal Shockwave Treatment: may be recommended help to stimulate regeneration to damaged or torn soft tissue.
Surgical Treatment for Achilles Tendonitis
In cases where either a conservative treatment has not resolved the problem or where a patient best or only treatment option is surgery, your doctor may recommend:
- Achilles Tendon Tear Repair - To Repair, Debride, Reconstruct and or Lengthen the Tendon
- Bursectomy - a surgical procedure done to remove an inflamed or infected bursa.
- Ostectomy - Removal of bony spurs from the heel which may be causing injury to the achilles tendon
Non Surgical Treatment for Achilles Tendon Ruptures
Non surgical treatment of achilles tendon ruptures is the mainstay of treating acute achilles tendon ruptures. A functional rehabilitation program (click here for protocol) results in a healed tendon with a good functional outcome. The overall length of treatment is 6-12 months. Treatment includes:
- Pain Medication-
Paracetamol or Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs) can relieve some pain or discomfort
- Casting / Boot: After an initial period of 2 weeks in a plaster, a specialised boot will be applied.
- Physiotherapy- A specialised functional rehabilitation program is recommended (click here for protocol)
Surgical Treatment for Achilles Tendon Ruptures
Surgical treatment is typically reserved for:
- Open injuries
- Late presentation ruptures (over 3 weeks)
- Chronic ruptures
Surgery for these cases can involve:
- Achilles Tendon Tear Repair
- Tendon Transfers: To help supplement the repair
Prevention of Achilles Tendon Problems
To help prevent an Achilles Tendon injury, it is a good practice to:
- Perform stretching exercises
- Undertake warm-up exercises before participating in any exercises or sports activities.
- Increase the intensity and length of time of activity.
- Undertake muscle conditioning around the ankle to help prevent injury