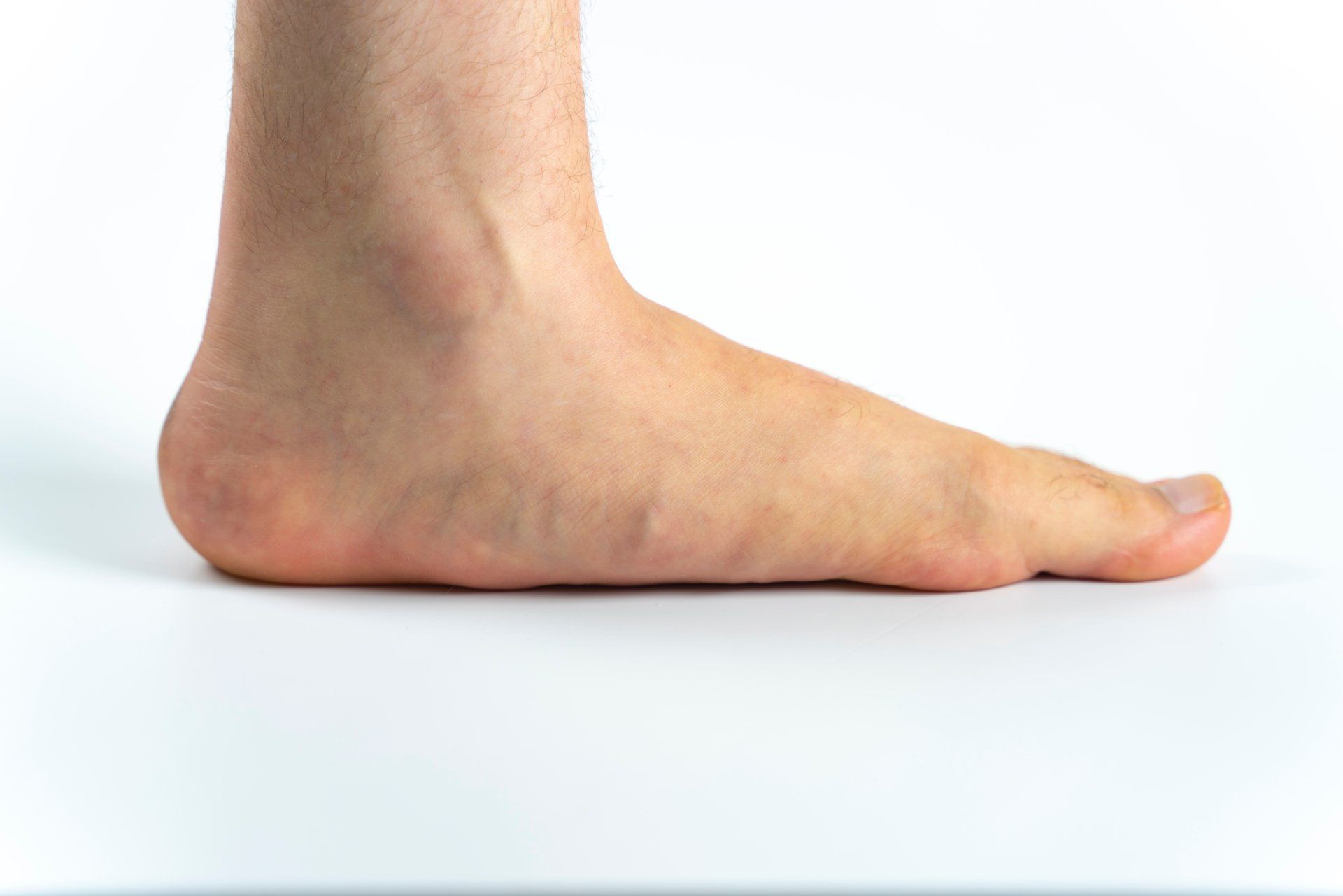
Flat Feet
What Are Flat Feet?
Flat feet are also commonly referred to as "fallen arches" or "pes planus", and occur when the feet roll in or over-pronation during standing or walking.
Flat Foot is a postural deformity in which the arch of the foot that runs lengthwise along the sole has collapsed to the ground or not formed at all.
This means the entire sole of the foot comes into complete or near-complete contact with the ground. With a healthy foot, the arch prevents the sole from lying flat on the ground while standing.
Who Does Flat Feet Affect?
Flatfoot is a common condition that can run in families.
Age is also a risk factor for Flat Feet. Arches can fall over time. Years of wear and tear can weaken the tendon that runs along the inside of the ankle and helps support the arch.
Flat Feet in Children
Flatfoot is normal in the first few years of life as the arch of the foot usually develops between the age of 3 and 5 years. In children, Flatfoot is often caused by loose connections between joints and excess baby fat deposits between foot bones which make the entire foot touch the floor while standing up.
As these pads diminish, the natural arch starts to develop between the ages of 3 to 6. However, 1 out of 10 children never develop the arch and they have flat feet through their adult years.
What is the Impact of Flat Feet or Collapsed Arches
With a healthy foot, the arch prevents the sole from lying flat on the ground while standing. Flat feet tend to cause another condition called overpronation, which is when the ankles roll inward while you're walking. This can lead to foot and ankle pain.
Because your feet are the basis of support for your entire body, having flat feet and overpronation can cause problems with your spinal alignment and cause aches and pains.
Flat feet will often cause your legs to turn unnaturally inward and can contribute to injuries often associated with overuse and stress such as:
- Shin Splints
- Back Problems
- Swollen Ankles
- Knee / Hip/ Back Problems, due to misalignment
- Plantar Fasciitis
- Metatarsalgia
- Tendonitis
- Bunions
Flat Feet discomfort can also reduce a patient's active lifestyle leading to more health problems and weight gain.
Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction (PTTD) is a condition caused by changes in the tendon, impairing its ability to support the arch. This results in flattening of the foot. PTTD is often called flatfoot because it is the most common type of flatfoot developed during adulthood.
What are the Causes of Flat Feet?
There are many conditions that can cause flat feet and overpronation. Common foot deformities and flexible muscle structure are the most frequent causes.
With age, the structure of the foot begins to collapse, causing the foot to flatten and adding stress to other parts of the foot.
Other conditions that can weaken the arch and lead to over-pronation include:
- Adult Flat Feet
- Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction (PTTD)
- Post Fracture (such as Lis Franc Injury)
- Obesity
- Diabetes
- Inflammatory disorders
- Paediatric Flat Feet
- Flexible Physiological
- Tarsal Coalition: In this condition, two or more bones of the foot join abnormally causing stiff and painful flat feet.
- Accessory Navicular
- Congenital Vertical Talus
- Inflammatory disorders
What are the Symptoms of Flat Feet?
Flat Feet do not always cause discomfort immediately, and some never suffer from any discomfort at all.
When symptoms do develop that can include:
- Pain during walking
- Pain in the heels causing difficulty with walking/running
- Feet and Calf Strain due to awkward alignment
- Inside arch of the foot is flattened
- Heel bone may be turned outward
- Heel or arch pain can worsen with activity
- Swelling along the inside of the ankle can also occur
- Discomfort with wearing shoes
- Inability to bear weight on the affected foot
- Tired, achy feet with prolonged standing or walking
- Pain in the foot, leg, knee, hip, or lower back
Stages of Flat Feet
If caught early enough Flat Feet can be corrected by treatments and supports.
- Stage 1 - there is pain along the posterior tibial tendon without deformity or collapse of the arch. The patient has the somewhat flat or normal-appearing foot they have always had.
- Stage II - a deformity from the condition has started to occur, resulting in some collapse of the arch, which may or may not be noticeable. The patient may feel it as a weakness in the arch. Many patients initially present in stage II, as the ligament failure can occur at the same time as the tendon failure and therefore deformity can already be occurring as the tendon is becoming symptomatic.
- Stage III - the deformity has progressed to the extent where the foot becomes fixed (rigid) in its deformed position.
- Stage IV - deformity occurs at the ankle in addition to the deformity in the foot.
How are Flat Feet Diagnosed?
The diagnosis of Flat Feet includes:
Medical History
Your doctor will ask questions about:
- Current symptoms and their severity
- If an injury was sustained
- Your medical history including family or genetic links
- Your current and past medications
- The impact of the problem on your occupation and lifestyle
Physical Examination
Your doctor perform comprehensive physical evaluation that will include:
- Examining the affected area for swelling, pain, bruising or other features
- Assessing your range of motion, walking pattern and other relevant features
Diagnostic Testing
Once your doctor has completed the physical examination further tests maybe required. These tests can help your doctor determine or eliminate possible causes. These can include:
- X-Ray
- Ultrasound (US)
- Computerised Tomography (CT)
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
Once a final diagnosis has been completed your doctor can discuss with you and recommend any treatment options.
Non Surgical Treatment for Flat Foot
Flat Feet can be treated conservatively with orthotic insoles that are designed with appropriate arch support to prevent the over-pronation. Stability shoes that feature a firm heel counter and wide soles help reduce over-pronation.
Treatment for Flat Feet can begin with:
- Rest: Rest the affected area as more damage could result from putting pressure on the injury.
- Strengthening your foot muscles through toe curls, heel raises, and other exercises to improve foot support, stability and shock absorption.
- Not walking barefoot: Always wear proper fitting and supportive shoes
- Avoiding running or other high-impact sports
- Shoe modification: Wearing a well-fitting, supportive shoe can help relieve aching pain caused by flatfoot.
If you still experience foot pain, and your quality of life is affected by over-pronation you should seek further help. Children with flatfoot that do not exhibit any other symptoms are monitored as they grow to assess for any changes. For symptomatic flatfoot, your doctor may suggest some of the following non-surgical treatments.
- Activity Modification: Avoid participating in activities that cause pain such as walking or standing for long periods of time.
- Orthotic Devices: Your surgeon may advise on the use of orthotic devices (arch support) that are worn inside the shoes to support the arch of the foot.
- Physical Therapy: Strengthening & Stretching exercises of the heel can provide pain relief.
- Medications: Pain relieving medications such as NSAID’s can help to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Shoe Modification: Using a well‐fitting, supportive shoe can help relieve aching pain caused by flatfoot.
Surgical Treatment of Flat Feet
While surgery is rarely needed to treat flatfoot, if conservative treatment options fail to relieve symptoms then surgery may be necessary to resolve the problem. Depending on the condition, various procedures may be performed including:
- Tendon Transfers
- Tendon Lengthening
- Joint Fusion
- Bone osteotomy
What if Flat Feet are left Untreated?
If Over-pronation of the feet is left untreated, they become progressively more painful and debilitating. This can lead to arthritis developing in the foot and ankle.